AOP
AOP
Spring의 핵심 개념중 하나인 DI가 애플리케이션 모듈들 간의 결합도를 낮춰준다면, AOP는 메소드를 만들어 그 메소드를 재사용하도록 도와주는 기법이다.
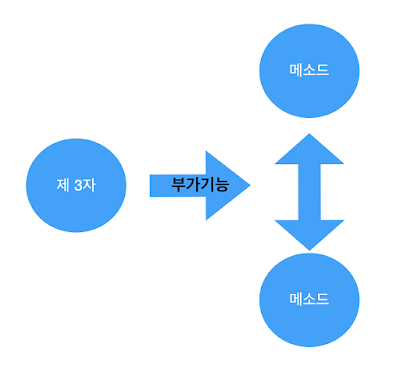
AOP (Aspect-Oriented Programming) 란 단어를 번역하면 관점 지향 프로그래밍이다. 보통 제 3자의 관점에서 바라본다라고 얘기한다.
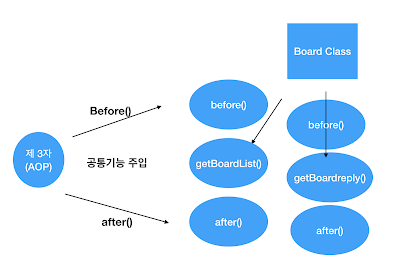
BoardClass 에 있는 getBoardList() 함수와 getBoardreply() 함수를 호출했을 때, 공통적으로 호출해야할 기능들이 있다고 해보자. 그럼 AOP(제3자)가 자동적으로 확인하고 공통기능들을 호출할 것이다.
AOP의 용어
-
타깃
타깃은 부가기능을 부여할 대상이다. 핵심기능을 담은 클래스일 수도 있지만 경우에 따라서는 다른 부가기능을 제공하는 프록시 오브젝트일 수도 있다.
-
어드바이스
어드바이스는 타깃에게 제공할 부가기능을 담은 모듈이다. 어드바이스는 오브젝트로 정의하기도 하지만 메소드 레벨에서 정의할 수도 있다. 어드바이스는 여러 종류가 있다. MethodInterceptor처럼 메소드 호출 과정에 전반적으로 참여하는 것도 있지만, 예외가 발생했을 때만 동작하는 어드바이스처럼 메소드 호출 과정의 일부에서만 동작하는 어드바이스도 있다.
-
조인 포인트
조인포인트란 어드바이스가 적용될 수 있는 위치를 말한다. 스프링의 프록시 AOP에서 조인 포인트는 메소드의 시행 단계뿐이다. 타깃 오브젝트가 구현한 인터페이스의 모든 메소드는 조인 포인트가 된다.
-
포인트컷
포인트컷이란 어드바이스를 적용할 조인 포인트를 선별하는 작업 또는 그 기능을 정의한 모듈을 말한다. 스프링 AOP의 조인 포인트는 메소드의 실행이므로 스프링의 포인트컷은 메소드를 선정하는 기능을 갖고 있다. 그래서 포인트컷 표현식은 메소드의 실행이라는 의미인 execution으로 시작하고, 메소드의 시그니처를 비교하는 방법으로 주로 이용한다. 메소드는 클래스 안에 존재하는 것이기 때문에 메소드 선정이란 결국 클래스 선정하고 그 안의 메소드를 선정하는 과정을 거치게 된다.
-
프록시
프록시는 클라이언트와 타깃 사이에 투명하게 존재하면서 부가기능을 제공하는 오브젝트다. DI를 통해 타깃 대신 클라이언트에게 주입되며, 클라이언트의 메소드 호출을 대신 바아서 타깃에 위임해주면서, 그 과정에서 부가기능을 부여한다. 스프링은 프록시를 이용해 AOP를 지원한다.
-
어드바이저
어드바이저는 포인트컷과 어드바이스를 하나씩 갖고 있는 오브젝트이다. 어드바이저는 어떤 부가기능(어드바이스)을 어디에(포인트컷) 전달할 것인가를 알고 있는 AOP의 가장 기본이 되는 모듈이다. 스프링은 자동 프록시 생성기가 어드바이저를 AOP 작업의 정보로 활용한다. 어드바이저는 스프링 AOP에서만 사용되는 특별한 용어이고, 일반적인 AOP에서는 사용되지 않는다.
-
애스펙트(Aspect)
OOP 클래스와 마찬가지로 애스펙트는 AOP의 기본 모듈이다. 한 개 또는 그 이상의 포인트컷과 어드바이스의 조합으로 만들어지며 보통 싱글톤 형태의 오브젝트로 존재한다. 따라서 클래스와 같은 모듈 정의와 오브젝트와 같은 실체의 구분이 특별히 없다. 두 가지 모두 애스펙트라고 불린다. 스프링의 어드바이저는 아주 단순한 애스팩트라고 볼 수 있다.
AOP 실습
순서
- SpringExample이라는 프로젝트를 만들고, package.com.tutorialspoint.ex 패키지를 생성 한다.
- 필요한 스프링 라이브러리를 External jars 추가 버튼을 눌러서 추가한다.
- aspectjrt.jar , aspectjweaver.jar , aspectj.jar 특정 라이브러리를 프로젝트에 추가한다.
- com.tutorialspoint.ex 패키지 밑에 Logging , Student , MainApp 클래스들을 생성한다.
- com.tutorialspoint.ex 패키지 안에 Beans.xml 빈설정 파일을 만든다.
- 마지막은 아래 설명대로 빈 설정파일이랑 자바 파일의 내용을 만들고 실행하는 것이다.
Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id = "log" ref = "logging">
<aop:pointcut id = "selectAll"
expression = "execution(* com.tutorialspoint.ex.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref = "selectAll" method = "beforeAdvice"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref = "selectAll" method = "afterAdvice"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref = "selectAll"
returning = "retVal" method = "afterReturningAdvice"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref = "selectAll"
throwing = "ex" method = "AfterThrowingAdvice"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!-- Student 클래스에 대한 빈-->
<bean id = "student" class = "com.tutorialspoint.ex.Student">
<property name = "name" value = "Zara" />
<property name = "age" value = "11"/>
</bean>
<!-- Logging 클래스에 대한 빈 -->
<bean id = "logging" class = "com.tutorialspoint.ex.Logging"/>
</beans>
Logging
package com.tutorialspoint.ex;
public class Logging {
/**
선택된 메소드 실행전에 호출 됨.
*/
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("Going to setup student profile.");
}
/**
선택된 메소드 실행 후에 호출됨
*/
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("Student profile has been setup.");
}
/**
선택된 메소드 실행 후 리턴됨.
*/
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal) {
System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString());
}
/**
선택된 메소드 실행후 Exception이 있다면 실행됨.
*/
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex) {
System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}
Student
package com.tutorialspoint.ex;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + age );
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
Mainapp
package com.tutorialspoint.ex;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/tutorialspoint/ex/Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
student.printThrowException();
}
}
Console Result
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:Zara
Going to setup student profile.
Age : 11
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:11
Going to setup student profile.
Exception raised
Student profile has been setup.
There has been an exception: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
AOP 지명자들
Pointcut Expression
pointcut expression은 @Pointcut 어노테이션의 값으로써 나타낼수 있다.
@Pointcut(“within(@org.springframework.stereotype.Reository * )”)
public void repositoryClassMethod() {}
포인트컷 시그니쳐는 이름을 제공해주는데 , advice 어노테이션이 해당 포인트컷을 참조할 때 사용된다.
@Around(“repositoryClassMethod()”)
public Object measureMethodExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
…
}
pointcut expression은 aop:pointcut 태그의 expression property의 값으로 나타낼 수 있다
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id =“anyDaoMethod”
expression=“@target(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository)”/>
</aop:config>
Pointcut 지명자들
Spring AOP에게 어떤 것을 가져올지 말해주는 키워드인 pointcut designator(PCD , 포인트컷 지명자)로 pointcut expression으로 시작한다. 여러가지 포인트컷 지명자가 있는데, 예를들어 메소드의 execution이나 타입 , 메소드 arguments, 또는 어노테이션이다.
- execution
Spring PCD의 기본적인 지명자는 execution 이다.
@Pointcut(execution(public String org.baeldungdao.FooDao.findById(Long))”)
이 포인트컷 예제는 정확히 FooDao 클래스의 findById 함수와 매치시킨다. 하지만 이런 방법은 유연하지가 않다. 비록 다른 리턴타입 , 파라미터들을 갖고 있지만 우리가 FooDao의 클래스에 있는 모든 메소드를 매치시켜보고 싶다고 생각해보자. 이럴 땐 와일드카드를 사용하면된다.
@Pointcut(“execution(* org.baeldung.dao.FooDao.*(..))”)
첫번째 와일드카드는 return 값을 전부 수용하고, 두번째 와일드카드는 모든 메소드를 수용하고, (..) 패턴은 모든 파라미터 갯수를 수용한다.
-
within
execution과 비슷한 방법으로 가은 결과를 얻을 수 있는 다른 방법이다. 특정한 타입의 조인 포인트만 매치시킬 수 있다.
@Pointcut(“within(org.baeldung.dao.FooDao)”)org.baeldung 패키지나 서브 패키지들을 매치시켜줄수 있다.
@Pointcut(“within(org.baeldung..*)”) -
this , target
this 는 bean 레퍼런스가 주어진 타입의 인스턴스를 매치시키는 조인포인트이다. 반면에 target 는 타켓 오브젝트가 주어진 인스턴스의 타입일때 매치시키는 조인포인트이다. 전자는 스프링 AOP가 CGLIB 기반 프록시를 생성할때 동작하며, 후자는 JDK기반 프록시가 생성될때 사용된다. 타켓 클래스가 다음과 같은 인터페이스를 구현했다고 가정해보자.
public class FooDao implements BarDao { ... }이런 케이스는 JDK 기반 프록시가 사용 되며 프록시 객체는 Proxy 클래스의 인스턴스가 될 것이고, BarDao 인터페이스를 구현하기 때문에 target PCD를 사용해야한다.
@Pointcut("target(org.baeldung.dao.BarDao)")반대로 FooDao가 proxyTargetClass 프로퍼티나 어떠한 인터페이스를 구현하지 않았다면, true 값으로 설정된다, 그러면 프록시 객체는 FoddDao의 서브클래스가 되고 this PCD 방법을 사용할 수 있다.
java @Pointcut( "target(org.baeldung.dao.BarDao)") -
args
특정한 메소드의 인자들을 매칭시켜주고 싶을 때 사용한다.
@Pointcut("execution(* *..find*(Long))")이 포인트 컷은 find라는 이름으로 시작하는 어떠한 메소드와 타입이 Long 인 하나의 파라미터로 구성되있는 메소만 매치시킨다. 만약 첫번째 파라미터는 Long 타입으로 갖고싶지만, 파라미터의 값들을 더 여러개 받고 싶다면 아래 나와 있는 표현식을 사용하면 된다.
@Pointcut("execution(* *..find*(Long,..))")