책임 연쇄 패턴
Chain Of Responsibility(책임 연쇄 패턴)
목적
책임 연쇄 패턴은 클라이언트의 요청을 처리하기 위해 객체를 체인 형태로 전달하여 결합력을 낮추기 위해 사용합니다. 체인 안에 있는 객체 자신이 요청을 어떻게 처리할지 결정하며 다음 체인으로 객체로 전달 할지 결정합니다.
자바에서 여러 개의 try-catch 블록이 책임 연쇄 패턴을 사용하고 있습니다. catch 블록이 처리 할 수 없으면, 요청을 그 다음 catch 블록으로 넘깁니다. 만약 마지막 catch 블록까지 갔음에도 불구하고 처리할 수 없다면, 해당 exception은 try-catch 밖으로 나가게 됩니다.
적용 포인트
어떤 요청을 여러 개의 핸들러나 요소로 처리해야 할 경우 사용하면 좋습니다.
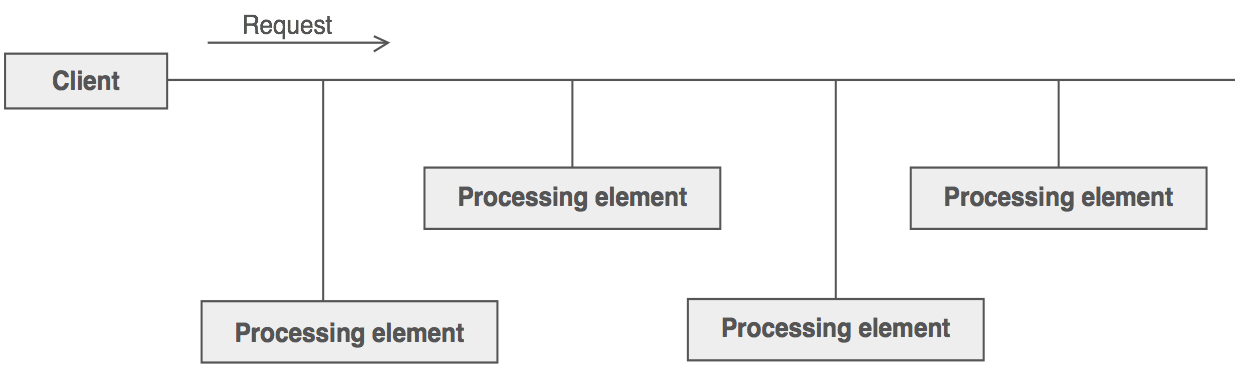
예제
책임 연쇄 패턴은 우리가 일상에서 돈을 뽑을 때 사용하는 ATM 기기와 같습니다. 돈을 인출할 때는 사용자가 인출할 돈의 양을 입력을 합니다. ATM 기기는 10만원,5만원,1만원 단위로 인출이 가능합니다.
만약 사용자가 천원 단위를 입력하면 오류가 납니다. 이 예제를 자바로 구현해보겠습니다.
사용할 기본 클래스와 체인 인터페이스
인출할 돈을 저장하는 클래스 Currency 클래스를 만들고 체인으로 사용할 인터페이스를 만들겠습니다.
Currency.java
public class Currency {
private int amount;
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public Currency(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
}
WithdrawChain.java
public interface WithdrawChain {
void setNextChain(WithdrawChain withdrawChain);
void withdraw(Currency currency);
}
인터페이스는 다음 처리기를 지정해주는 setNextChain()과 요청을 처리할 withdraw() 메소드가 있습니다.
체인 구현
WithdrawChain 을 구현해서 각각 다른 처리기를 만들어 withdraw 메소드를 구현해야 합니다. ATM 기에는 10만원권, 5만원권, 1만원권만 인출할 수 있으므로, 총 3개의 구현 클래스가 나와야 합니다.
Withdraw100000Won.java
//십만원
public class Withdraw100000Won implements WithdrawChain {
//Withdraw50000Won 체인 연결
private WithdrawChain withdrawChain;
@Override
public void setNextChain(WithdrawChain nextChain) {
this.withdrawChain = nextChain;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(Currency currency) {
if(currency.getAmount() >= 100000) {
int num = currency.getAmount()/100000;
int remain = currency.getAmount() % 100000;
System.out.println("10만원짜리 " +num+"장이 인출되었습니다.");
if(remain != 0) this.withdrawChain.withdraw(new Currency(remain));
} else {
this.withdrawChain.withdraw(currency);
}
}
}
Withdraw50000Won.java
//오만원
public class Withdraw50000Won implements WithdrawChain {
//Withdraw10000Won 체인 연결
private WithdrawChain withdrawChain;
@Override
public void setNextChain(WithdrawChain nextChain) {
this.withdrawChain = nextChain;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(Currency currency) {
if(currency.getAmount() >= 50000) {
int num = currency.getAmount()/50000;
int remain = currency.getAmount() % 50000;
System.out.println("5만원짜리 " +num+"장이 인출되었습니다.");
if(remain != 0) this.withdrawChain.withdraw(new Currency(remain));
} else {
this.withdrawChain.withdraw(currency);
}
}
}
Withdraw10000Won.java
//만원
public class Withdraw10000Won implements WithdrawChain {
private WithdrawChain withdrawChain;
@Override
public void setNextChain(WithdrawChain nextChain) {
this.withdrawChain = nextChain;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(Currency currency) {
if(currency.getAmount() >= 10000) {
int num = currency.getAmount()/10000;
int remain = currency.getAmount() % 10000;
System.out.println("1만원짜리 " +num+"장이 인출되었습니다.");
if(remain != 0) this.withdrawChain.withdraw(new Currency(remain));
} else {
this.withdrawChain.withdraw(currency);
}
}
}
withdraw 메소드 구현이 가장 중요합니다. 모든 withdraw 구현들은 요청을 인출할 금액에 따라 처리합니다.
만약 한 처리기가 전부 다 처리를 못하면, 남은 요청을 체인안에 있는 다음 처리기로 보냅니다. 만약 처리기가 아무 것도 처리를 못해도, 그 요청 전부를 다음 체인으로 넘깁니다.
체인 만들기
이 부분이 체인을 만드는데 가장 중요한 순서 입니다.
조심해야 할 점은 처리기 순서를 1만원 -> 5만원 -> 10만원 순서로 하면, 모든 돈이 만원 권으로 나오기 때문에 두번 째 처리기는 사용하지 않아 불필요하게 됩니다.
ChainOfResponsibilityTests.java
public class ChainOfResponsibilityTests {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WithdrawChain withdraw100000Won = new Withdraw100000Won();
WithdrawChain withdraw50000Won = new Withdraw50000Won();
WithdrawChain withdraw10000Won = new Withdraw10000Won();
withdraw100000Won.setNextChain(withdraw50000Won);
withdraw50000Won.setNextChain(withdraw10000Won);
while(true) {
System.out.println("인출 할 돈을 눌러주세요");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int money = scanner.nextInt();
Currency currency = new Currency(money);
withdraw100000Won.withdraw(currency);
System.out.println("--------------");
}
}
}
결과
인출 할 돈을 눌러주세요
50000
5만원짜리 1장이 인출되었습니다.
--------------
인출 할 돈을 눌러주세요
130000
10만원짜리 1장이 인출되었습니다.
1만원짜리 3장이 인출되었습니다.
--------------
인출 할 돈을 눌러주세요
70000
5만원짜리 1장이 인출되었습니다.
1만원짜리 2장이 인출되었습니다.
--------------
UML

정리
- 클라이언트는 요청이 어느 부분의 체인에서 처리되고 있는지 알 수 없고, 체인에 있는 첫번 째 객체로만 요청을 보냅니다.
- 체인에 있는 각 객체는 요청을 처리하기 위한 자신만의 구현을 갖고 있습니다. 다음 체인으로 요청을 전부 또는 부분만 보냅니다.
- 체인에 있는 모든 객체는 반드시 요청을 전달하기 위한 다음 처리기를 참조하고 있어야 합니다. 구성기법을 사용하고 있습니다.
- 체인을 만들 때는 조심해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 요청이 처리기에 전달되지 않거나 요청을 처리할 객체가 체인이 없을 수 없습니다.
-
책임연쇄패턴은 객체의 결합력을 낮추는데 좋지만, 구현 클래스가 많이 필요하고 유지보수성이 높아진다는 트레이드 오프가 있습니다.
- java.util.logging.Logger#log() 과 javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter() 이 책임연쇄패턴을 사용하고 있습니다.
